Wednesday W.O.W - Bitcoin Mining 💰₿⛏️
[5 min read] Your mid-week bite sized treat on emerging tech on our journey to the Metaverse. Learn how fresh Bitcoin is made by using computing power to validate transactions and secure the network.
A nibble of knowledge in your inbox every Wednesday with a simple format:
🇼 What the technology is.
🇴 Objective(s) - what is it trying to achieve, with some examples
🇼 Why it is important.
This is week 43 of the 520 weeks of writing I have committed to, a decade of documenting our physical and digital lives converge.
🇼 What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin, the granddaddy of digital currencies, has dominated headlines and ignited debates worldwide. But what exactly is Bitcoin mining, and why is it so crucial to the functioning of this “digital gold”?
At its core, Bitcoin mining is the process by which new Bitcoins are created and transactions on the Bitcoin network are verified and added to the blockchain, the underlying technology that records all Bitcoin transactions. The term "mining" might evoke images of pickaxes and tunnels, but in the digital realm, it's an entirely different beast. Bitcoin operates on a decentralised ledger, also known as a blockchain. This ledger is maintained by a network of computers, known as miners. These miners play a pivotal role in ensuring the security and reliability of Bitcoin transactions.
Here's how it works: When someone initiates a Bitcoin transaction, it's added to a pool of unconfirmed transactions. Miners, who dedicate their computational power to the network, compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. This process is known as Proof of Work (PoW). The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to validate the block of transactions, add it to the blockchain, and is rewarded with newly created Bitcoins and transaction fees. This entire process, known as mining, is crucial to the very existence of Bitcoin.
🇴 What are its Objectives?
Now that we've covered the basics of Bitcoin mining, let's discuss its objectives and importance in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
1. Security: Bitcoin mining ensures the security and immutability of the blockchain. Solving these cryptographic puzzles is no easy feat, and it requires an immense amount of computational power. This level of security makes it exceptionally challenging for malicious actors to alter the transaction history or engage in fraudulent activities.
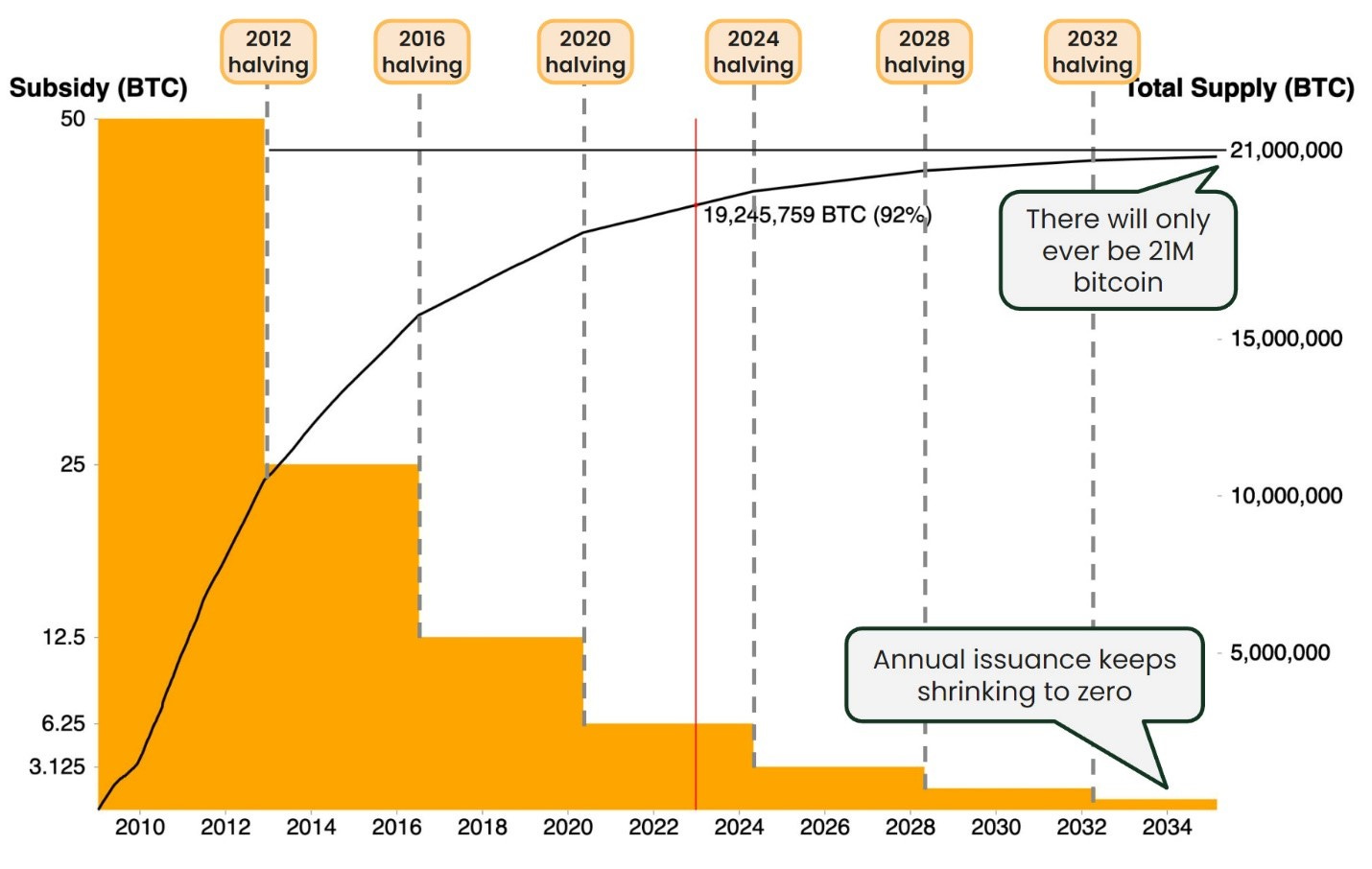
2. Issuance of New Bitcoins: Bitcoin mining is the mechanism through which new Bitcoins are created and introduced into circulation. This controlled issuance follows a predetermined hardcoded schedule of halving issuance every four years (orange columns below). It’s like a digital central bank with inflation reducing like clockwork, unlike traditional fiat currencies are subject to inflation by governments printing more and more money.
3. Transaction Verification: Miners validate and confirm Bitcoin transactions. Without miners, the network would rely solely on trust, making it susceptible to fraud and double-spending. Through the PoW process, miners reach a consensus on which transactions are legitimate and which aren't.
4. Decentralisation: Bitcoin's decentralisation is a cornerstone of its philosophy. Anyone with the required hardware and software can become a miner, making it a truly inclusive system. This decentralisation prevents any single entity from controlling the network, enhancing its resilience. Bitcoin doesn’t have a CEO or board to sue. It can’t be shut down, or effectively banned, or controlled by an elite.
🇼 Why could Bitcoin mining have a role to play in the future of our economy?
As Bitcoin continues to grow and evolve, there are two major ways that the mining process could hold implications for the future of our society.
1. Energy Innovation: Bitcoin mining has been criticised for its energy consumption, however this narrative is starting to unwind. From Bitcoin mining on-site of renewable energy production to capture energy surplus, to electrical grid stabilisation, mining has spurred innovation potentially accelerating our transition to a greener future. Some even foresee the Bitcoin narrative becoming “ESG friendly” over the coming years as the likes of giant asset managers like Blackrock start accumulating Bitcoin aggressively to potentially boost the performance of the somewhat lacklustre ESG Stocks category.
2. Financial Inclusion: Bitcoin's decentralised nature allows access to the financial system for millions worldwide who are unbanked or underbanked. By participating in Bitcoin mining, individuals can actively engage with this new financial ecosystem, especially in places where electricity is cheap. Through Bitcoin and mining, we can extend financial services to regions without access to traditional banking infrastructure. This could empower individuals and communities, reducing economic disparities.
Bonus: Hear from a NZ startup leading the way in renewable Bitcoin mining
On the latest Weekly Journal, the watch of the week was a fund that invests in the infrastructure needed to convert landfill waste into energy and conducting bitcoin mining on-site.
Another NZ team pioneering this space is Stackr, a Bitcoin mining company harnessing sustainable and renewable energy sources. Examples would be using hydro, wind and solar generated electricity that is surplus to demand and otherwise difficult to store. Another example is using plant waste from forestry (which would otherwise rot and release methane) as biochar. By incinerating this material and generating heat, power can be generated by a Stirling engine.
You can read all about it on page 41 of the latest issue of Digital Assets Investor magazine:
That’s all for this week! If you have any organisations in mind that could benefit from learning about emerging technology, be sure to reach out. Educational workshops are one of many consulting services I offer.