Weekly Journal: 2025 Nobel Prize in Physics Honours Quantum Breakthrough That Powers the Digital and Metaverse Era
[6 min read] Your weekend guide to getting ahead on the digital frontier. From a metaverse perspective, this recognition underscores how quantum physics and immersive computing are converging.

Welcome to this week’s Weekly Journal 📔, your guide to the latest news & innovation in emerging technology, digital assets, and our exciting path to the Metaverse. This is week 149 of the 520 weeks of newsletters I have committed to, a decade of documenting our physical and digital lives converge. New subscribers are encouraged to check out the history & purpose of this newsletter as well as the archive.
- Ryan
🌐 Digital Assets Market Update
To me, the Metaverse is the convergence of physical & virtual lives. As we work, play and socialise in virtual worlds, we need virtual currencies & assets. These have now reached mainstream finance as a defined asset class:
🔥🗺️Heat map shows the 7 day change in price (red down, green up) and block size is market cap.
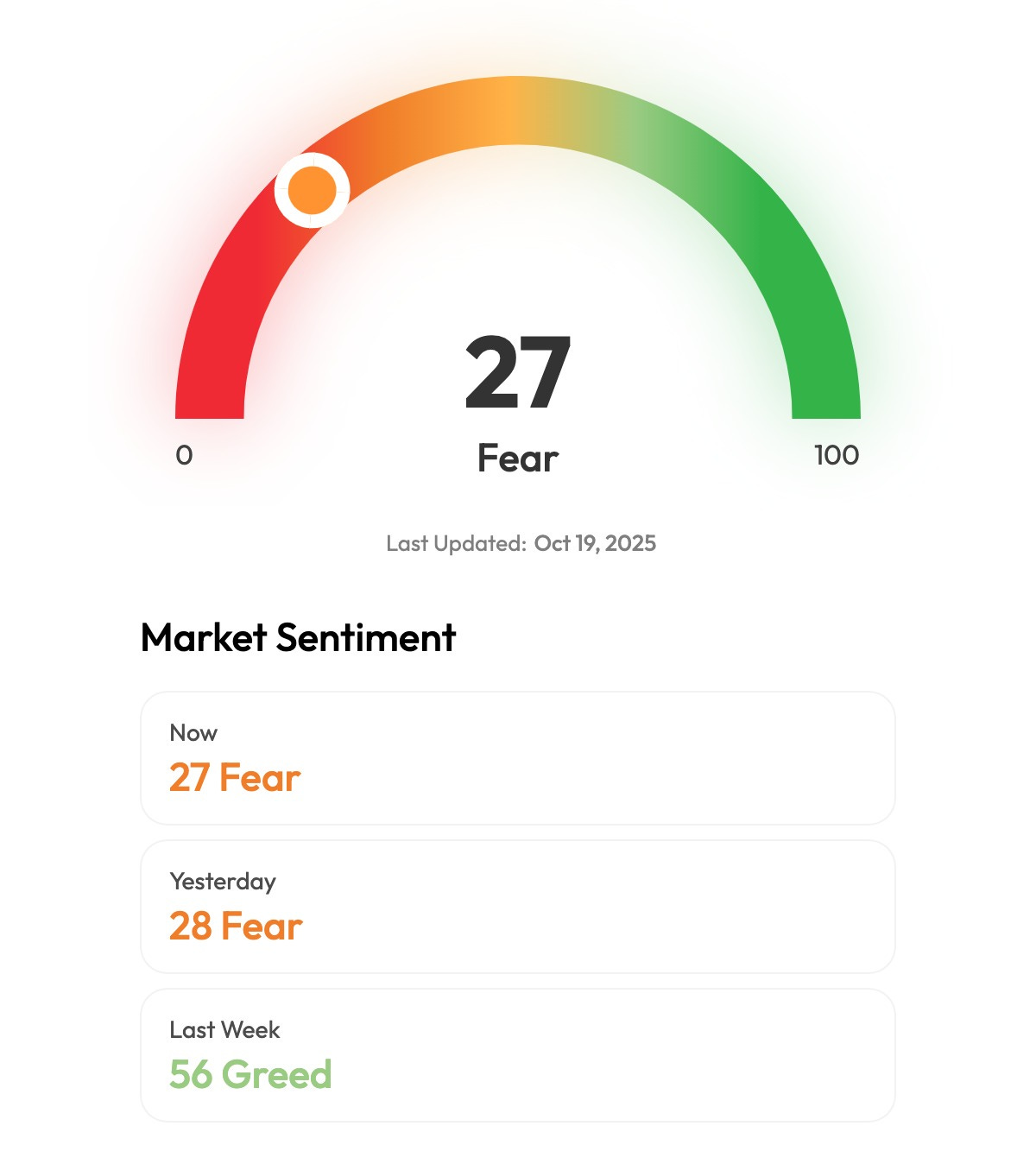
🎭 Crypto Fear and Greed Index is an insight into the underlying psychological forces that drive the market’s volatility. Sentiment reveals itself across various channels—from social media activity to Google search trends—and when analysed alongside market data, these signals provide meaningful insight into the prevailing investment climate. The Fear & Greed Index aggregates these inputs, assigning weighted value to each, and distils them into a single, unified score.
🗞️ Metaverse news from this week:
2025 Nobel Prize in Physics Honours Quantum Breakthrough That Powers the Digital and Metaverse Era
The 2025 Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to John Clarke, Michel H. Devoret, and John M. Martinis for their pioneering work in macroscopic quantum tunnelling and energy quantisation in electric circuits — discoveries that underpin much of today’s quantum computing revolution.
Their experiments proved that quantum mechanical behaviour can manifest on a visible, macroscopic scale, bridging the gap between the atomic world and the devices we hold in our hands. As the Nobel Committee put it, quantum mechanics remains “the foundation of all digital technology.”
The trio’s research not only unlocked the physics behind quantum processors, superconducting qubits, and ultra-sensitive sensors, but also laid the groundwork for emerging technologies like quantum cryptography, communications, and photonics—all of which will be critical to the next-generation internet and metaverse infrastructure.
From a metaverse perspective, this recognition underscores how quantum physics and immersive computing are converging. Quantum circuits promise to deliver the processing speed, security, and simulation power required to sustain massive, persistent virtual worlds. As classical computing nears its limits, the metaverse’s evolution into a truly real-time, high-fidelity ecosystem will likely depend on the quantum discoveries celebrated by this year’s Nobel laureates.
“One of the underlying reasons cellphones work is because of all this work,” Clarke noted — a fitting reminder that every digital leap, from smartphones to the metaverse, ultimately stands on quantum ground.
⚛️ Quantum Foundations of the Metaverse
1. Quantum tunnelling: instant data flow across barriers
The phenomenon honoured by the 2025 Nobel Prize — quantum tunnelling — allows particles to pass through energy barriers they shouldn’t be able to cross. In digital systems, this principle enables superconducting circuits and ultra-fast transistors, the invisible engines of VR, AR, and AI computation. In the metaverse era, tunnelling will underpin quantum processors that move data almost instantaneously between worlds.
2. Energy quantisation: computing with nature’s smallest units
The discovery that electric circuits have discrete, quantised energy levels forms the basis of qubits, the building blocks of quantum computers. These will eventually simulate real-world physics — light, matter, weather, and motion — so that the digital and physical merge seamlessly.
3. Quantum sensors: precision beyond pixels
Advances in quantum measurement allow sensors to detect magnetic, gravitational, and photonic changes at atomic precision. This translates into hyper-accurate spatial tracking, biometrics, and environmental rendering, vital for fully embodied metaverse experiences.
4. Quantum cryptography: security for virtual economies
Quantum mechanics ensures that certain information can’t be copied or intercepted without detection. As value moves onchain, quantum-secure communication will safeguard identity, assets, and data across immersive platforms.
5. Quantum entanglement: the metaverse’s ultimate connective tissue
Entanglement — the mysterious linkage between particles across any distance — hints at future quantum networks where information transfer occurs without traditional latency. Such networks could enable true real-time presence between users anywhere on Earth, or even off it.
📖 Read of the week: How Quantum Computing Will Upend Cybersecurity — and Why Web3 Might Survive It
🗞 By Jean-François Bobier, Clément Fouilloux, Vanessa Lyon, Dirk Stegemann, Gildas Bouteiller & David Panhans | Boston Consulting Group | 15 October 2025
Quantum computing is advancing fast enough to make security professionals uneasy — and for good reason. As the Boston Consulting Group warns, the arrival of powerful quantum processors will render today’s encryption obsolete, threatening the cryptographic foundations of everything from banking systems to the metaverse’s digital economies.
The coming challenge:
Quantum machines don’t just compute faster — they compute differently. Algorithms such as Shor’s could, once scaled, break RSA and elliptic-curve cryptography, the very methods used to secure identities, assets, and communications across the web. BCG estimates that by the mid-2030s, quantum systems could realistically decrypt data we consider secure today.
For metaverse builders and Web3 architects, this isn’t a distant problem. These immersive networks depend on persistent trust frameworks — digital identity, asset ownership, cross-world payments — all of which rely on classical encryption. If compromised, entire economies of virtual goods, stablecoins, and smart contracts could be exposed.
The positive side:
The good news is that many of the world’s most advanced decentralised networks are already moving to quantum-resistant standards:
🔐 Bitcoin Core developers have been researching post-quantum signatures, including lattice-based and hash-based cryptography, to safeguard long-term network integrity.
🌐 Ethereum and major L2 chains are experimenting with zk-proof upgrades and quantum-secure key rotation models.
💾 NIST’s post-quantum cryptography initiative — now entering global adoption — will anchor many of these future-proof systems.
Meanwhile, the metaverse itself could benefit from quantum computing in other ways: simulating materials, powering digital twins, enhancing AI agents, and even securing vast distributed networks through quantum key distribution (QKD).
Why it matters:
BCG’s piece is less a warning and more a wake-up call — urging enterprises and governments to embrace “crypto agility”: the ability to evolve security protocols before quantum disruption hits. For decentralised ecosystems, that adaptability is already in their DNA.
The takeaway:
Quantum computing will transform cybersecurity, but it doesn’t have to destroy it. The next decade will determine whether the metaverse becomes vulnerable — or whether it emerges as a quantum-secure network of digital worlds, ready for the challenges of the post-encryption era.
🔗 Read the full article on BCG
🎥 Watch of the week:
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2025 was awarded jointly to John Clarke, Michel H. Devoret and John M. Martinis for the discovery of macroscopic quantum mechanical tunnelling. What on earth does that mean?
AI Spotlight 🎨🤖🎵✍🏼: Are We Living in a Golden Age of Stupidity — or Standing at the Threshold of a Cognitive Renaissance?
In the Metaverse, AI will be critical for creating intelligent virtual environments and avatars that can understand and respond to users with human-like cognition and natural interactions.
The Guardian’s Sophie McBain paints a sobering picture of the modern mind under siege. From MIT experiments showing reduced brain activity when students use ChatGPT to teachers lamenting AI-fuelled shortcuts, it seems technology is making thinking itself optional. Our “frictionless” world rewards passivity — a state of continuous partial attention, where we skim, scroll, and outsource our memory, creativity, and even curiosity. It’s little wonder “brain rot” became Oxford’s word of the year.
Yet beneath the handwringing lies a paradox — and perhaps a hopeful one. Human intelligence has always evolved through offloading: writing, calculators, and search engines once inspired the same fears. Each tool that freed us from rote recall made space for deeper abstraction. The problem isn’t AI itself, but our relationship with it. Used well, AI could become the greatest cognitive amplifier in history, sharpening—not dulling—our collective mind.
Imagine classrooms where AI tutors adapt to each learner’s rhythm, workplaces where digital agents handle routine tasks so humans can innovate, and metaverse learning environments that cultivate critical thinking through immersion rather than automation.
As the MIT researchers suggest, our brains need friction to learn—but friction can be designed into technology, too. The next chapter of the AI age may depend on doing just that: building systems that don’t think for us, but think with us.
So perhaps this isn’t a golden age of stupidity after all — but the messy, necessary adolescence of a smarter, more collaborative intelligence, one where human creativity and machine capability finally learn to grow together.
That’s all for this week! If you have any organisations in mind that could benefit from keynotes about emerging technology, be sure to reach out. Public speaking is one of many services I offer.